Table of Contents
In this blog, we will explore what semantic SEO actually means and why it matters in today’s digital marketing world for ranking higher, increasing engagement, and boosting conversions through your content. You’ll also get a practical, step-by-step guide on how to implement semantic SEO in your own writing to improve topical authority and relevance for users.
And to make everything even easier to understand, I will explain the concept using a simple “Coffee beans” example so you can understand and learn semantic SEO without any confusion.
What is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is the modern SEO approach of optimizing content based on user intent. That means instead of relying on keyword repetition, it uses topic clusters, semantic keywords, and structured data to help search engines interpret content more accurately.
This improves relevance, ranking for long-tail queries, and topical authority. It ensures content answers complete user queries, aligns with conversational search, and becomes eligible for rich snippets, AI overviews, and voice search results. By addressing all related aspects of a topic, your content becomes more valuable for users and search engines alike.
Semantic SEO is heavily influenced by Google algorithms like Hummingbird, RankBrain, BERT, and MUM, which focus on understanding the meaning behind queries rather than just matching keywords. It also leverages structured data from Schema.org and connections in the Knowledge Graph to build stronger topical authority.
What are Semantic Keywords?
Semantic keywords are words and phrases that are closely related in meaning to your main keyword. They help search engines understand the context, intent, and topic depth of your content.
They aren’t just synonyms, they include:
- Related concepts
- Entities (people, places, brands)
- Attributes
- Actions/verbs connected to the topic
- Questions users commonly ask
- Variations of search intent
Comparison Between Normal SEO vs Semantic SEO
If we have to explain the difference between Normal SEO and Semantic SEO in one line, then it will be:
Normal SEO is keyword-focused.
Semantic SEO is topic-focused.
Normal SEO Example
Keyword: “best coffee beans”
A normal SEO article would:
- Repeat the keyword multiple times
- List 5-10 coffee beans
- Write a short buying guide
It only targets one keyword.
Semantic SEO Example
Topic: “best coffee beans”
A semantic SEO article would cover:
- All Related Semantic Keywords (premium coffee beans, high-quality coffee beans, top-rated coffee beans, strong coffee beans, coffee beans with rich flavor, low-acidity coffee beans, best coffee beans online, affordable premium coffee, top coffee brands)
- Types of coffee beans (Arabica, Robusta, Liberica)
- Roast levels (light, medium, dark)
- Grind size
- Brewing methods (espresso, pour-over, French press)
- Flavor notes
- Storage tips
- How to choose beans based on taste
- FAQs
It targets the entire topic, not just one keyword.
How to Optimize Content Using Semantic SEO
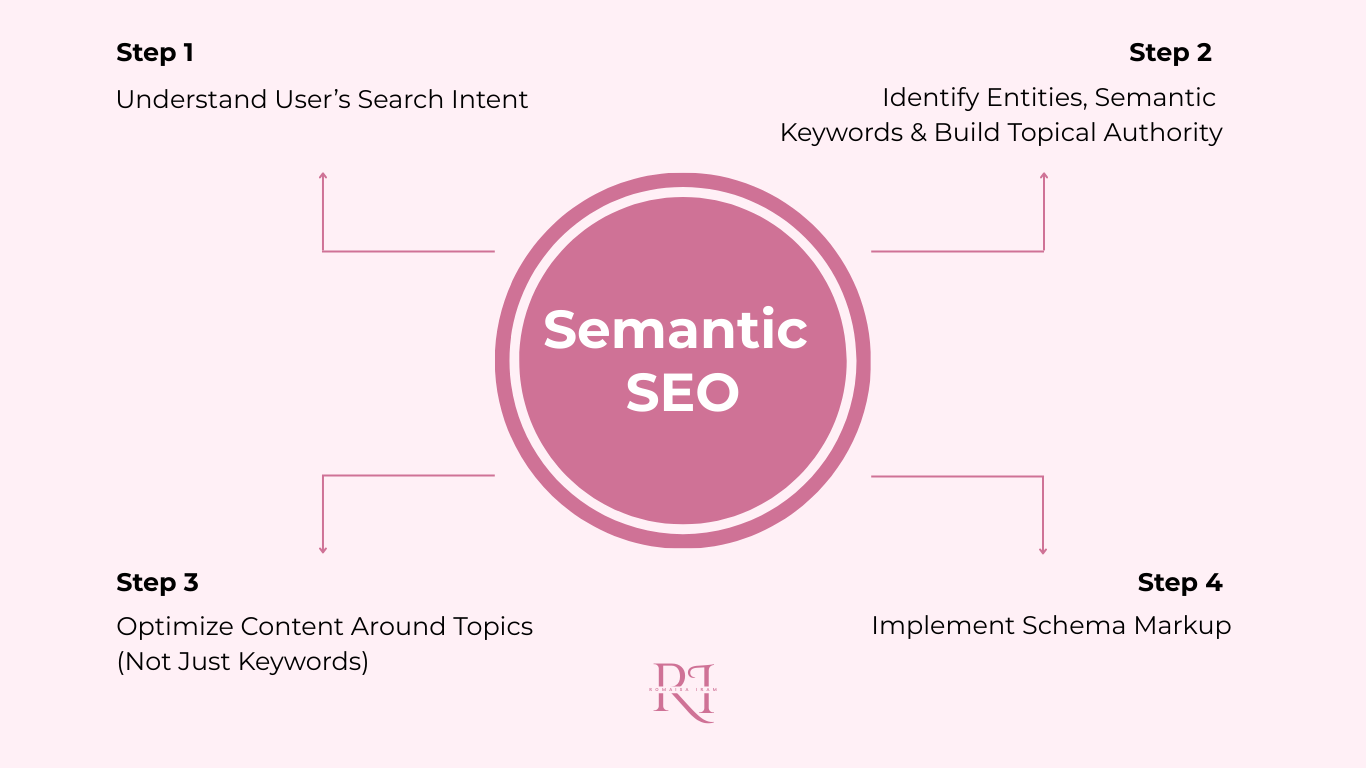
Optimizing for semantic SEO requires a structured, multi-step approach that goes beyond keyword research. Here’s an enhanced 4-step process that makes your content more discoverable by Google, SGE, and AI search systems:
Step 1: Understand User’s Search Intent
To optimize the content properly, you have to understand the user’s search intent. For this
- Analyze the deeper purpose behind the query. Like, is the user looking to learn, compare, buy, or solve a problem?
- For understanding this, study the intent behind queries using entities, search patterns, and SERP behavior.
- Categorize your content into any one of the 4 different Intent categories, including
- Informational: Example, “What are Arabica coffee beans?”
- Commercial: Example, “Best coffee beans for espresso.”
- Transactional: Example, “Buy roasted coffee beans online.”
- Navigational: Example, “ABC Coffee Cafe menu.”
Understanding this ensures your content answers not just the query but the entire reason behind it.
Tip: Use People Also Ask, Google Autosuggest, AI Overviews, and competitor pages to understand every angle of user intent.
Best Practices for Website Pages
Each page should have one clear purpose and one intent.
- Homepage can use commercial and light transactional elements.
- Service pages should remain strictly transactional (hire, buy, contact).
- About page should stay informational (story, trust, expertise).
- Contact page should be purely transactional (form, email, details).
- Clear intent helps Google understand your site and improves user experience.
Best Practices for Blog Pages
- Keep one primary search intent (usually informational).
- You may include a small supporting intent only if it naturally fits the topic.
Example
Main intent: “What are coffee beans?” (Informational)
You can ADD a small section like:
“Best brands for buying coffee beans” (Commercial)
- Avoid mixing opposite intents like:
- Informational and Transactional
- Commercial and Transactional
- Navigational with anything
- Opposite goals (education and selling in the same blog)
- Keep content focused, structured, and aligned with one keyword cluster.
- Write to satisfy user questions clearly so Google sees strong relevance.
Step 2: Identify Entities, Semantic Keywords & Build Topical Authority
This step focuses on mapping the entities, related keywords, and concepts, and building topical clusters that Google expects to see when ranking authoritative content.
- Identify Core & Supporting Entities
Entity-based SEO is the core of semantic optimization.
You must identify:
- Primary entities (e.g., Coffee beans, Espresso, Roast level)
- Related concepts (e.g., acidity levels, brewing method, Arabica vs Robusta)
- Contextual layers (e.g., origin country, flavor profile, grind size)
This helps search engines understand the depth of your content.
- Extract Semantic Keywords & Attributes
Include LSI keywords, synonyms, and related attributes. For this, use NLP-based tools like Google NLP API, Semrush, Ahrefs, Surfer NLP, or GPT to find:
- Semantic keywords
- Contextual phrases
- Descriptive modifiers
- Attributes related to the topic
These terms guide your writing toward natural, context-rich language rather than keyword stuffing.
- Build Topical Clusters
Organize your subtopics into meaningful clusters. Each cluster should answer a different dimension of the main topic, allowing you to cover the subject holistically.
Example clusters: bean types, roast levels, brewing techniques, flavor profiles.
- Identify Content Gaps
Analyze competitor pages to find subtopics, questions, or entities they’ve covered, but you haven’t. Adding these completes your topical coverage and improves your authority.
- Check Knowledge Graph Relevance
Look for entities already recognized by Google’s Knowledge Graph. Integrating these increases your content’s alignment with how Google understands the topic.
By the end of this step, you’ll have a clear semantic map including entities, clusters, attributes, and content gaps that becomes the foundation of intelligent, high-performance content creation.
Step 3: Optimize Content Around Topics (Not Just Keywords)
With your semantic map ready, the next step is turning that research into structured, valuable content that answers user intent thoroughly. This is where semantic SEO becomes powerful.
Your goal is to create content that answers:
- The user’s main question
- All related sub-questions
- All context behind the topic
- All the problems users may face
To do that:
- Create Topically Complete Content
Instead of chasing isolated keywords, write content that addresses:
- The main question
- Important sub-questions
- Necessary background information
- Challenges users may face
This makes your page the most comprehensive resource on the subject.
- Use Semantic Language Naturally
Integrate the entities, attributes, and semantic keywords from Step 2. These reinforce your topic without repetition or keyword stuffing.
- Structure Content Based on User Intent
Use clear headings that reflect how users search:
- Informational intent
- How-to intent
- Comparison intent
- Problem-solving intent
This improves readability and strengthens semantic relevance.
- Strengthen Internal Linking
Connect your page to other relevant pages in your cluster. Internal links help Google understand your topic depth and support your site-wide authority.
- Add Helpful Enhancements
Make your content more engaging and semantically rich with:
- Examples and definitions
- Visuals or diagrams
- Comparison tables
- Step-by-step breakdowns
- Flowcharts
- FAQ’s
- Short checklists
These improve user experience and content clarity.
- Include an FAQ Section
Finish with well-chosen FAQs based on long-tail queries and voice-search style questions. This broadens your semantic coverage and captures additional rankings.
This step turns your research into a polished, well-structured, and search-friendly piece of content that satisfies both users and algorithms.
Step 4: Implement Schema Markup
Add structured data about entities and topics on your page. This is also called Technical Semantic SEO. Schema markup helps AI and search engines understand your content, not just read it.
Add structured data wherever relevant:
- Article Schema for blogs, guides, news
- FAQ Schema for question-based sections
- Product Schema for product or service pages
- Organization Schema for brand credibility
- How-To Schema for instructions and step-by-step guides
- Breadcrumb Schema for better navigation
This improves your chances of ranking in:
- Featured Snippets
- Google SGE (AI Overviews)
- People Also Ask
- Carousels & Knowledge Panels
- Shopping Results
Structured data is becoming essential for AI-driven search (Google SGE & Bing Copilot), not optional.
Combine Semantic and Traditional SEO for Maximum Results
Semantic SEO works best when paired with traditional fundamentals:
- Engaging meta titles/descriptions
- Clean URL structure
- Image alt text
- Optimized headings and titles
- Fast-loading pages
- Strong internal linking
This hybrid approach creates content that Google can easily understand, AI can accurately summarize, and users find engaging, resulting in higher readability, stronger conversions, and lasting impact.
Benefits of Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO is more than a trend; it’s a necessity for long-term online success. It helps in
- Building Stronger Topic Authority: Search engines prefer pages that cover all aspects of a topic. By building comprehensive content, your page becomes a trusted resource.
- Improved user engagement: Visitors stay longer when their questions are fully answered. This reduces bounce rate and improves user metrics, which in turn boost rankings.
- Increased conversions: Content matches user intent better, leading to leads, subscriptions, or sales.
- Enhanced AI & Voice Search Visibility: Semantic SEO optimizes your content for AI and voice search. This means it’s more likely to appear in:
- Google AI Overviews
- ChatGPT answers
- Gemini responses
- Voice assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant
- Long-Term Ranking Stability: Unlike traditional SEO, which relies on keywords, semantic SEO focuses on meaning and context, making your content less vulnerable to algorithm updates.
- Higher rankings for complex queries: Ranks for long-tail, conversational, and natural-language searches.
Conclusion
Now you know how semantic SEO works and how to implement it. Feel free to use the concepts from this guide to optimize your own content. After applying these Semantic SEO steps consistently, your content will start ranking for more keywords, perform better in AI search, and drive higher engagement.
But if you want expert support to execute this for your website or brand with precision and depth, you can reach out. I would love to help you optimize your content strategy and boost your organic growth.
FAQ’s
Q: What are entities in SEO?
An entity is a real-world thing, concept, or idea that Google can identify and understand.
Entities are not just words; they represent people, places, products, brands, technologies, or concepts that have meaning in the real world. These entities are used in Entity-based SEO.
Examples of Entities
People: Elon Musk, Serena Williams
Companies/Brands: Google, Apple, Semrush
Products/Services: iPhone 15, ChatGPT, Starbucks Coffee
Concepts: Semantic SEO, Machine Learning, Climate Change
Locations: Paris, Dubai, Islamabad
Q: What is entity-based SEO?
Entity-based SEO is a strategy where content is optimized around recognized entities and their relationships instead of just keywords, helping Google connect your content to real-world topics and build topical authority.
Q: What is a Knowledge Graph and why is it important?
The Knowledge Graph is Google’s database of entities and facts. Linking your content to entities recognized in the Knowledge Graph helps search engines understand your content better and improves ranking for complex queries.
Q: What are topical clusters and how do they help SEO?
Topical clusters are groups of related subtopics organized around a main topic. They build topical authority, show Google you cover a subject comprehensively, and improve rankings for multiple related queries.
Q: What is Schema.org and why should I use it?
Schema.org provides structured data markup to make your content machine-readable. Adding schemas (FAQ, Product, How-To, Article) helps Google and AI systems understand entities and topics, which can improve visibility in rich snippets and AI search results.
Q: What are Google Hummingbird, RankBrain, BERT, and MUM?
These are Google algorithms and AI models that focus on understanding the meaning behind queries rather than just matching keywords. They help Google deliver more relevant and conversational search results.
Q: How does NLP in SEO work?
NLP (Natural Language Processing) allows search engines to analyze language and context in content. Using NLP-friendly content, such as entity relationships and semantic keywords, helps your page rank better in AI-powered search results.
Q: What is Google SGE (Search Generative Experience)?
Google SGE is Google’s AI-powered search system that summarizes content and provides direct answers. Optimizing for Semantic SEO and structured data increases your chances of being featured in AI overviews.